What is Waste-to-Energy

Waste-to-energy (WtE) or energy-from-waste (EfW) is the production of electricity, heat, or fuel from urban and industrial waste. Waste-to-energy technologies convert non-recyclable waste into energy. Superheated steam is produced from the combustion of waste in boilers, and the steam drives turbo generators to produce electricity. Environmental Impacts of Waste-to-Energy would refer the understanding about the relationship of waste Management.
Harnessing Energy from Waste
Energy can be generated from waste materials by converting them into usable forms, such as electricity or heat. Various methods exist for generating energy from waste, including incineration, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. Waste materials can be burned for heat, converted into synthetic gas, or broken down into biogas in an oxygen-free environment. It is possible to use waste-to-energy in everyday life to generate renewable energy for homes, businesses, and even vehicles. Waste disposal can also be reduced by minimizing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
What are the environmental impacts of waste?
Air, water and soil pollution is caused by inadequate waste management, including non-existent collection systems and ineffective treatment. Contaminated drinking water can be contaminated by littering and unsanitary waste, which can also cause illness and infection. It causes multifaceted environmental problems that damage ecosystems, human health and natural resources.
Impacts of Poor Waste Management and Fossil Fuels on Environmental
Poor waste management in importing countries can degrade soil and water quality, increase air pollution, or harm biodiversity and overall ecosystem health. Wasted energy exacerbates climate change and depletes non-renewable resources. Fossil fuels used to produce energy release greenhouse gases such as CO2 and methane. Methane is 28 times more effective at trapping heat than CO2, thus adding to global warming.


What are the Advantages of Waste-to-Energy Systems
Renewable Energy Generation
One of the main advantages of waste-to-energy systems is their contribution to the production of renewable energy. Australia, as a country committed to sustainable energy goals, can benefit greatly from this technology. By harnessing the energy potential of waste, energy recovery systems help reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources and promote a cleaner energy mix. This not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also contributes to a greener, more sustainable future for Australia.
Waste Diversion and Reduction
Waste-to-energy systems are essential for diverting and reducing waste. Rather than disposing of waste in landfills, which can cause environmental issues and space constraints, these systems transform waste into valuable resources. This technology aids in preserving land resources and reducing the environmental consequences of landfill use by diverting waste away from them. Additionally, waste-to-energy facilities can efficiently handle the growing amount of waste produced in cities, preventing landfills from becoming overwhelmed.
Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction
Australia faces the challenge of reducing greenhouse gas emissions to combat climate change. Waste-to-energy systems can contribute to this effort by reducing methane emissions from landfills. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is released when organic waste decomposes in landfills. By redirecting this waste and converting it into energy, waste-to-energy systems reduce methane emissions. In addition, burning waste in waste-to-energy plants also helps reduce carbon dioxide emissions, further contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Resource Recovery and Recycling
Waste-to-energy systems promote resource recovery and recycling. Ahead of the energy gender transition valuable materials such as metals, plastics and glass can be extracted from waste. This not only reduces dependence on raw resources but also supports a circular economy. By recovering and reusing materials that would otherwise be thrown away, waste-to-energy systems help conserve natural resources and minimize the need for further mining. This waste-to-energy aspect is also consistent with the waste management hierarchy in Australia, which prioritizes waste reduction, reuse and recycling over waste treatment.
Economic Benefits
There are several economic benefits to implementing waste-to-energy systems. First, it creates employment opportunities and stimulates economic growth. The creation and operation of waste-to-energy facilities requires a highly skilled workforce, creating employment opportunities for local communities. Additionally, waste management, including energy recovery, can generate revenue for municipalities. By using waste as a resource, municipalities can sell the energy produced and offset the costs associated with waste management. Ultimately, waste-to-energy systems will save municipalities money in the long run by reducing the need for landfills and related costs.
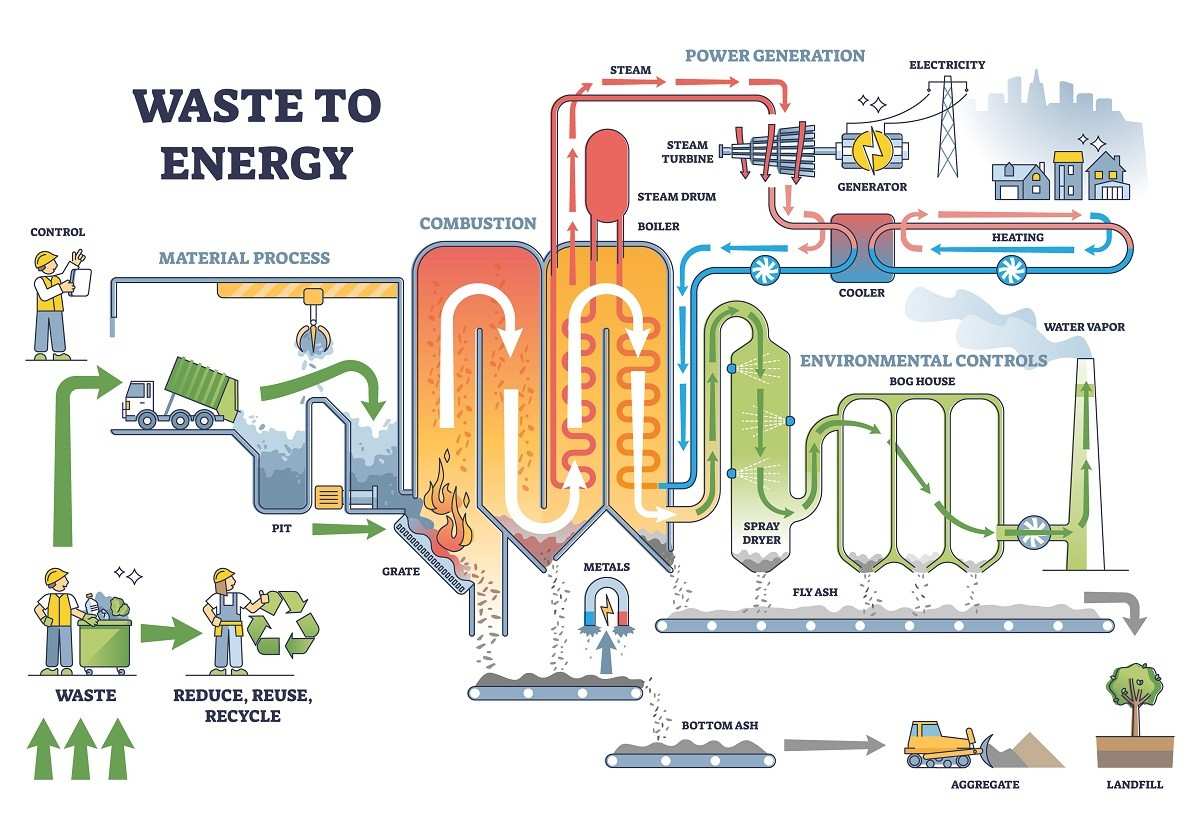
What Methods enhance Waste-to-Energy
Burning Trash for Electricity
Incinerating waste to produce electricity, also referred to as waste-to-energy, is the process of converting non-recyclable waste into heat, electricity, or fuel. Initially, municipal solid waste is gathered and recyclable items are separated. Subsequently, the leftover waste is burned at elevated temperatures, producing steam that is used to generate electricity.
Enhancing Sustainability Through Technological Advancements and Regulations
The advantages of this approach include the reduction of landfill usage, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and decreased reliance on fossil fuels. Nevertheless, challenges such as air pollution and the presence of toxic ash residue remain. Despite these obstacles, advancements in technology and environmental regulations have enhanced the sustainability of waste-to-energy techniques for electricity production.
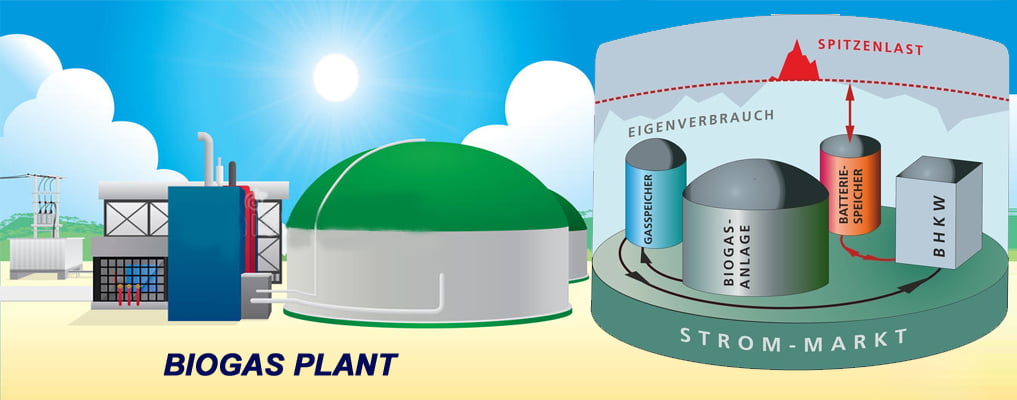
Garbage into Gas
Waste-to-energy technology utilizes various methods to convert garbage into gas for energy production. These methods encompass thermal, biological, and non-combustion processes, effectively transforming different types of waste, including municipal solid waste, landfill gas, and wastewater sludge, into clean and renewable energy sources. A significant advantage of this technology is its ability to reduce the volume of waste in landfills, thereby minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental pollution.
Benefits and Challenges of Waste-to-Energy Systems
This approach contributes to sustainable waste management while providing a dependable source of renewable energy. Nevertheless, the implementation of waste-to-energy systems comes with its own set of challenges. These include the handling of toxic emissions and the control of potential air pollution. Additionally, high initial investment costs and public acceptance pose common obstacles. Despite these challenges, waste-to-energy systems offer a promising solution to address the growing energy demand and environmental concerns.
Fuel from Waste
Energy recovery methods convert waste into usable energy sources such as electricity, heat, or fuel. One approach is anaerobic digestion, in which microorganisms break down organic waste to produce biogas. Thermal conversion technologies such as incineration and gasification can also produce energy from waste. These methods can reduce the amount of waste that goes to landfill and provide a renewable energy source. They also help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and produce clean energy.
Integrating Waste-to-Energy Solutions
However, challenges include emissions control, public perception and operating costs. Despite these challenges, waste-to-energy can become part of everyday life through initiatives such as community composting programs, residential biogas digesters, and Power plants turn waste into energy. Integrating waste-to-energy into everyday life can help communities support environmental sustainability and energy independence.
Less Trash in Landfills
Waste-to-energy technology plays a crucial role in minimizing the amount of waste in landfills. By converting non-recyclable waste into energy, it effectively reduces landfill volume and generates renewable energy. This approach enables municipalities and communities to mitigate their impact on landfills and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Waste-to-Energy Technologies in Sustainable Waste Management
The advantages of waste-to-energy methods encompass the generation of renewable energy, decreased waste disposal in landfills, and the potential for cost savings. Nevertheless, there are challenges associated with this approach, including the need for substantial capital investment, environmental impacts stemming from emissions, and concerns regarding public safety. Despite these challenges, waste-to-energy technologies continue to hold significant importance in sustainable waste management.
Creates Clean Energy
Incineration is one method of generating energy from waste. In this process, municipal solid waste is burned at high temperatures, resulting in the production of steam. This steam is then utilized to power turbines, which generate electricity. Another approach is anaerobic digestion, where microorganisms break down organic waste such as food scraps and manure to produce biogas. This biogas can be utilized as a renewable energy source.
Challenges, and Its Role in Sustainable Energy
Waste-to-energy initiatives contribute to the production of clean energy by reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and generating electricity from non-renewable sources. Additionally, it helps decrease greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution by converting environmental impacts of waste-to-energy. However, there are certain challenges associated with waste-to-energy, including high initial investment costs, potential environmental impacts, and concerns regarding safety and health implications of waste incineration. Despite these obstacles, waste-to-energy remains a viable solution for sustainable waste management and the production of clean energy.
Can Save Money
There are multiple ways in which waste-to-energy can result in cost savings. Firstly, it helps in reducing the volume of waste that goes into landfills, which can be quite costly to manage. By converting waste into energy, there is a reduced dependence on conventional energy sources, resulting in financial savings for both individuals and businesses.
Reducing Costs and Generating Revenue
Moreover, businesses and local governments can generate their own electricity and heat, thereby reducing their energy expenses. Additionally, implementing waste-to-energy systems can lead to lower disposal costs and the possibility of generating revenue by selling surplus energy. This approach proves to be both practical and financially advantageous for waste management and reducing energy expenditures.
What are the Common Challenges with Waste-to-Energy
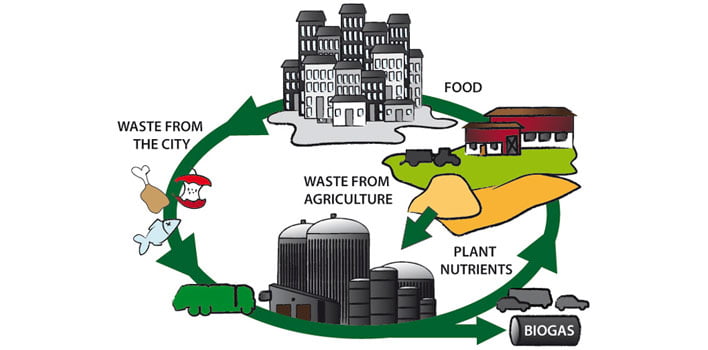
Cost to Set Up
Initial costs to set up a waste-to-energy system can vary. It includes costs related to equipment, land, construction and permits. Once the system is operational, there will be ongoing costs for labor, maintenance, fuel and waste disposal. The upfront costs often outweigh the potential long-term benefits and savings.
Cost Savings, Environmental Benefits, and Long-Term Viability
These benefits include reduced dependence on traditional energy sources, lower waste management costs, and potential revenue from energy sales. Waste-to-energy systems contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and providing an alternative to landfills. Despite the initial and ongoing costs, the potential savings and long-term benefits make it a viable and sustainable investment.
Real Places Where Waste-to-Energy Works
Waste-to-energy technology is being used in many places worldwide. Cities and industrial facilities have integrated this technology into their daily operations by using advanced methods to convert waste into usable energy. Embracing waste-to-energy has led to benefits such as less waste in landfills, sustainable waste management, and renewable energy for homes and businesses. It has also helped reduce greenhouse gas emissions and minimize environmental impact, making it a viable solution for sustainable energy needs.
How We Can Use Waste-to-Energy in Everyday Life
Waste-to-energy practices can easily be integrated into daily routines by participating in recycling programs, properly disposing of organic waste, separating recyclables from general waste, and composting food scraps. Supporting waste-to-energy initiatives can be achieved by advocating for the construction of waste-to-energy facilities and voicing support at local meetings.
Education and Integration into Household and Commercial Energy Solutions
Additionally, educating others about the benefits of these technologies helps build community support. Waste-to-energy technology can also be incorporated into household and commercial energy usage through biogas production from organic waste and combining renewable energy technologies for sustainable energy solutions.
FAQ
What is waste-to-energy?
Waste to energy is the process of generating energy in the form of electricity or heat from the initial waste treatment process. This involves the combustion or anaerobic digestion of organic waste. Examples include incineration and biogas production from landfill gas.
How does waste-to-energy work?
Waste to energy works by converting waste into heat, electricity or fuel through processes such as incineration, gasification or anaerobic digestion. For example, combustion uses combustion to produce steam to power turbines that produce electricity.
What are the benefits of waste-to-energy?
Turning waste into energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, reduce waste in landfills and produce renewable energy. It also promotes local economic growth and job creation. For example, a waste-to-energy plant in Palm Beach County, Florida produces enough electricity to power 44,000 homes.
What types of waste can be used for waste-to-energy?
Potential wastes for energy recovery include municipal solid waste, agricultural waste, sewage sludge, and certain types of industrial waste such as paper, cardboard, and wood.
How is waste-to-energy different from traditional waste disposal methods?
Energy recovery converts waste into electricity or heat, thereby reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills. Traditional methods involve disposal in landfills or incineration without energy recovery. For example, burning waste without energy recovery only produces ash, while energy recovery produces electricity.

Pingback: Solar Energy vs Fossil Fuels: A Comparison - Carbon Revolve
Pingback: How to Convert Plastic PET Bottles to Yarn? - Carbon Revolve
Sustainable waste recovery on farms is an essential practice for reducing environmental impact and promoting resource efficiency. Solar energy offers a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By integrating solar power into agricultural operations, farmers can achieve greater energy independence and cost savings. The comparison between solar energy and fossil fuels highlights the long-term benefits of renewable energy sources. How can we further encourage the adoption of solar energy in the agricultural sector? WordAiApi